WHAT IS CHLOREXIDINE?
Chlorhexidine is a molecule synthesized for the first time in 1950 as an antiseptic for mucous membranes, skin and wounds and used as a preservative in ophthalmic pharmaceutical formulations.
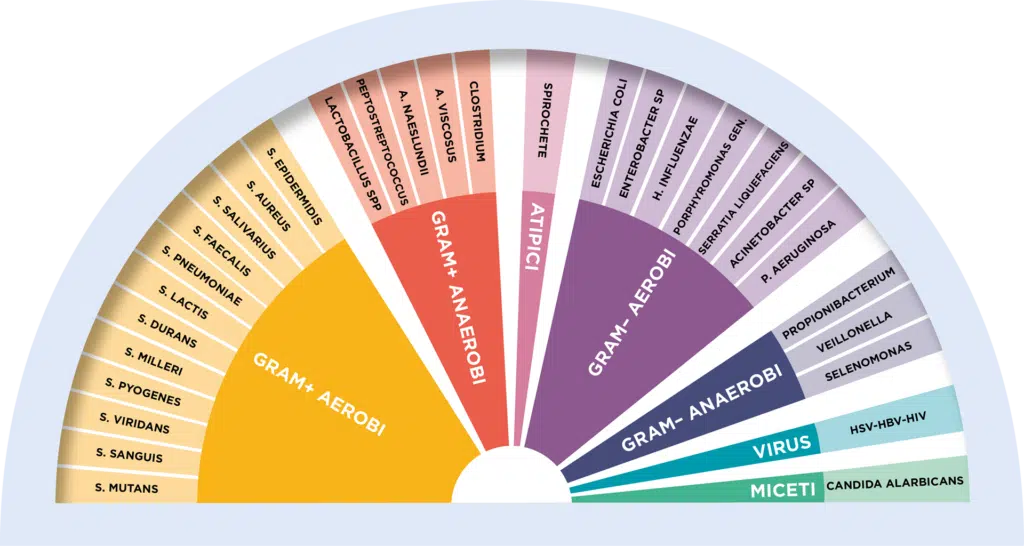
Chlorhexidine has been used in dentistry for over thirty years and is still considered the gold standard recognized throughout the world in plaque control and the prevention of gingivitis. Chlorhexidine, in fact, is not only able to break down the bacterial biofilm, but inhibits its formation and stratification. Furthermore, it has a large spectrum of action which makes it effective against Gram+ and Gram-, viruses and fungi; It has antifungal properties and does not induce bacterial resistance phenomena in the oral cavity. Finally, among the pluses of Chlorhexidine there is substantivity, i.e. the property of remaining bound to hard and soft tissues for 8/12 hours, allowing prolonged action and effectiveness throughout the day.
SIDE EFFECTS OF CHLORHEXIDINE
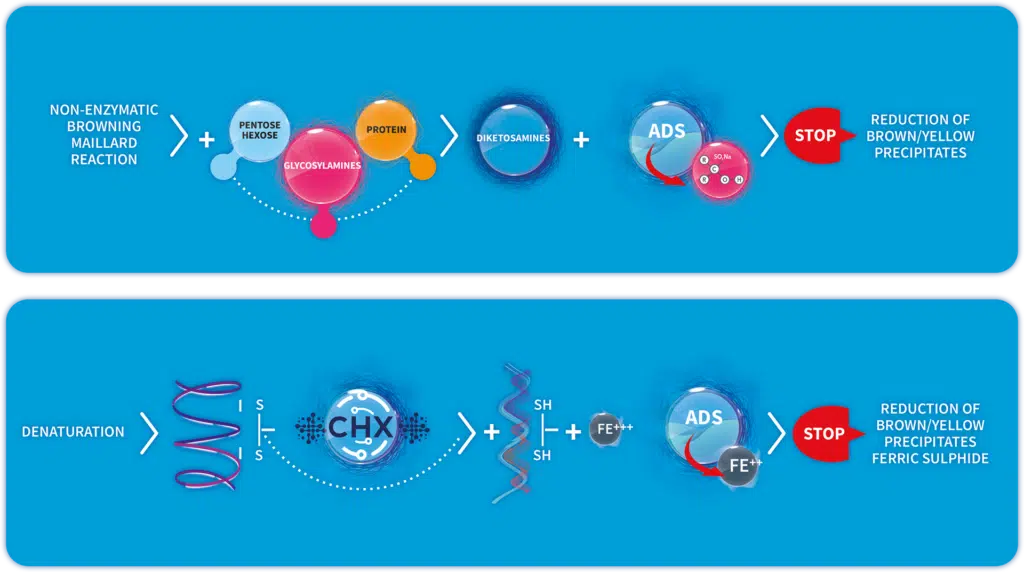
However, despite many advantages, chlorhexidine has an annoying side effect: it triggers chemical reactions in the oral cavity responsible for the pigmentation of the dental surfaces, thus decreasing the patient’s adherence to the treatment. In the past, this aesthetic alteration has led the professional to prescribe it with reservations and has compromised the patient’s compliance in the use of this active ingredient.
For this reason, the launch of Curasept ADS marked an epochal milestone in the history of oral care: a line of products in which the effectiveness of chlorhexidine was combined with the ADS system (Anti Discoloration System) capable of limiting the pigmenting action while preserving the effects of the treatment.